Malaysia Higher Education
With more than 30 years of experience in international education, Malaysia’s unique, well-structured higher education system offers you the opportunity to purse an international qualification at competitive rates. Malaysia hosts more than 100 institutions – both public and private – including foreign branches of reputable universities from the United States, United Kingdom, Australia and Ireland. The latter are offered either at their own overseas branch campus or in partnership with a Malaysian institution. You can choose US, UK, Irish, Australian or Malaysian academic qualifications designed with flexibility and affordability in mind.
1. Public Institutions
Public institutions are government-funded higher education institutions under the purview of the Ministry of Education Malaysia. They can generally be divided into three major categories as follows:
- Public universities offer undergraduate and postgraduate programmes, and sometimes pre-university foundation year and diploma courses. They can be divided into 3 major groups i.e. Research Universities, Focused Universities and Comprehensive Universities. There are currently 20 such institutions.
- Polytechnics and community colleges which offer programmes at certificate and diploma.
- Public colleges which offer certificate and diploma level programmes.
2. Private Universities
There are currently 41 private universities you can choose from that offer programmes at every level of studies, comparable to their public counterparts. Compared to university colleges and colleges, universities often have bigger campus and student facilities, conduct extensive postgraduate research programmes, and award degrees in their own names.
3. University Colleges
Compared to universities, university colleges usually have smaller-sized campuses and lower student numbers. Private university colleges usually run programmes at all levels, although they usually have fewer faculties and have a stronger focus on undergraduate programmes compared to postgraduate ones. Students who choose to obtain a degree awarded by a reputable foreign university usually have the flexibility to spend their time either fully in Malaysia or spend a year abroad at the awarding university’s home campus.
4. Accredited Training Centres
Accredited skills training centres are institutions registered under the Department of Skills Development that run training courses to equip students with specialised technical and vocational skills. Accredited by the Malaysian government, such courses provide pathways that enable students to gain internationally-recognised qualifications, such as by City and Guilds (UK), Confederation of Tourism, Hotel and Catering Management (UK), LCCI (UK), TAFE (Australia), and other international and professional bodies
5. Language Centre
Education institutions that fall under this category primarily offer language courses, although some of them also offer computer literacy training and other skills training.
6. International Branch Campuses
Get the best of international education in Malaysia by enrolling at the Malaysian branch campus of a foreign university! Malaysia took a step forward in internationalisation of higher education by opening its doors for reputable foreign universities to set up their campuses in Malaysia. Currently there are 10 foreign branch campuses that originate from Australia, United Kingdom, Ireland and China. These universities – some of which are in the top 100 of QS World University Rankings – offer programmes identical in structure and content to those at their home campuses. Enrolling at a foreign branch campus in Malaysia is good value for money where despite saving up to 40% on tuition fees and living costs, you will still get the same qualification as those studying at the home campus abroad.
7. College
Colleges in Malaysia are usually privately-owned institutions that do not have their own degree-awarding power. Even so, they are usually allowed to award qualifications from other institutions, including via twinning programmes with reputable foreign universities from the UK, Australia and USA. Some colleges also offer qualifications from professional bodies such as CLP, ACCA, ICAEW, CAT, and GCE A-Levels. Whilst the campus size and student numbers might be smaller, colleges usually come with excellent facilities comparable to that of universities and university colleges. Just like universities, colleges can only offer programmes accredited by the Malaysian Qualifications Agency.
Quality Assurance
When deciding the merit of each institution, you may want to look into its SETARA and MyQuest ratings. Each ratings employ a comprehensive and rigorous methodology to assess an education institution’s core functions or quality criteria. Compared to international rankings which are more outward-looking, SETARA and MyQuest ratings do not provide ranking but rather detailed quality assessment following visits and in-depth inspections by auditors.
SETARA rating was developed under the Malaysian Education Blueprint 2015-2025 for Higher Education for institutions of university and university college status, with the earlier category being further divided into mature and emerging universities. Each institution category is given its own weightage for core functions – namely teaching, research and services – so that unique strengths and challenges which are specific to each category’s niche are fairly represented.
MyQuest rating, on the other hand, is an instrument to evaluate the performance of institutions of college status in Malaysia. Developed in 2009, it focuses on 5 quality criteria which are students, programmes, graduates, resources and governance.
Both SETARA and MyQuest ratings are necessary to ensure students have the necessary tool to make an informed decision when choosing their education path. You can also read more on SETARA rating and MyQuest rating to know more.
Malaysian Qualifications Agency
Known as the MQA, it is a statutory body established under the Malaysian Qualifications Act 2007 to accredit academic programmes offered by all higher educational institutions, which is compulsory. This provides another level of comfort of the quality of a course especially in terms of its content and teaching materials, delivery mechanism and teaching staff experience.
Malaysia and World University Rankings
The Government of Malaysia spends around 5% its GDP on education – which is above the world and regional average – as a way to demonstrate the country’s highest regard for it. With the society’s unwavering belief in outstanding education, Malaysian school teachers are among the world’s most dedicated educators. The government also commissions the Higher Education Leadership Academy (AKEPT) to develop a solid talent pipeline for higher education institutions, to produce high-calibre academics or the top leaderships alike, as well ensuring good governance of institutions.
Other than grants from the government, Malaysian universities raise funds from industry collaboration which further enhances their research profile and their graduates’ employability. Investments from the private sector also led to the establishment private institutions and international campuses of foreign universities, some of which are also award-winning universities.
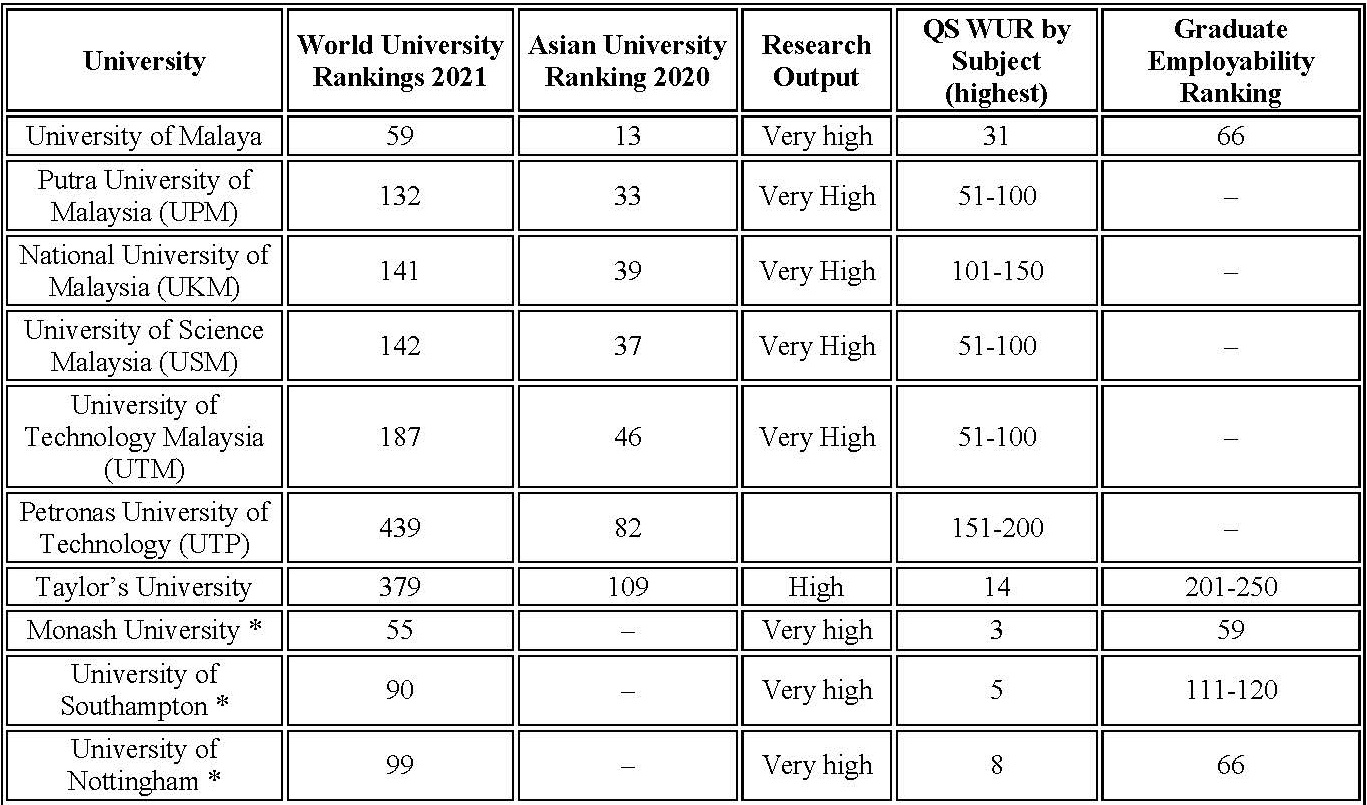
Coupled with a strong culture of excellence, Malaysia has a youth literacy rate of above 97%; gross enrolment ratio in tertiary education of 44.1% – higher than the global average; and proudly boasts 10 universities among the world’s top 500 of universities (a total of 23 in the top 1,000) according to Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) World University Rankings (WUR).

Your Comment :